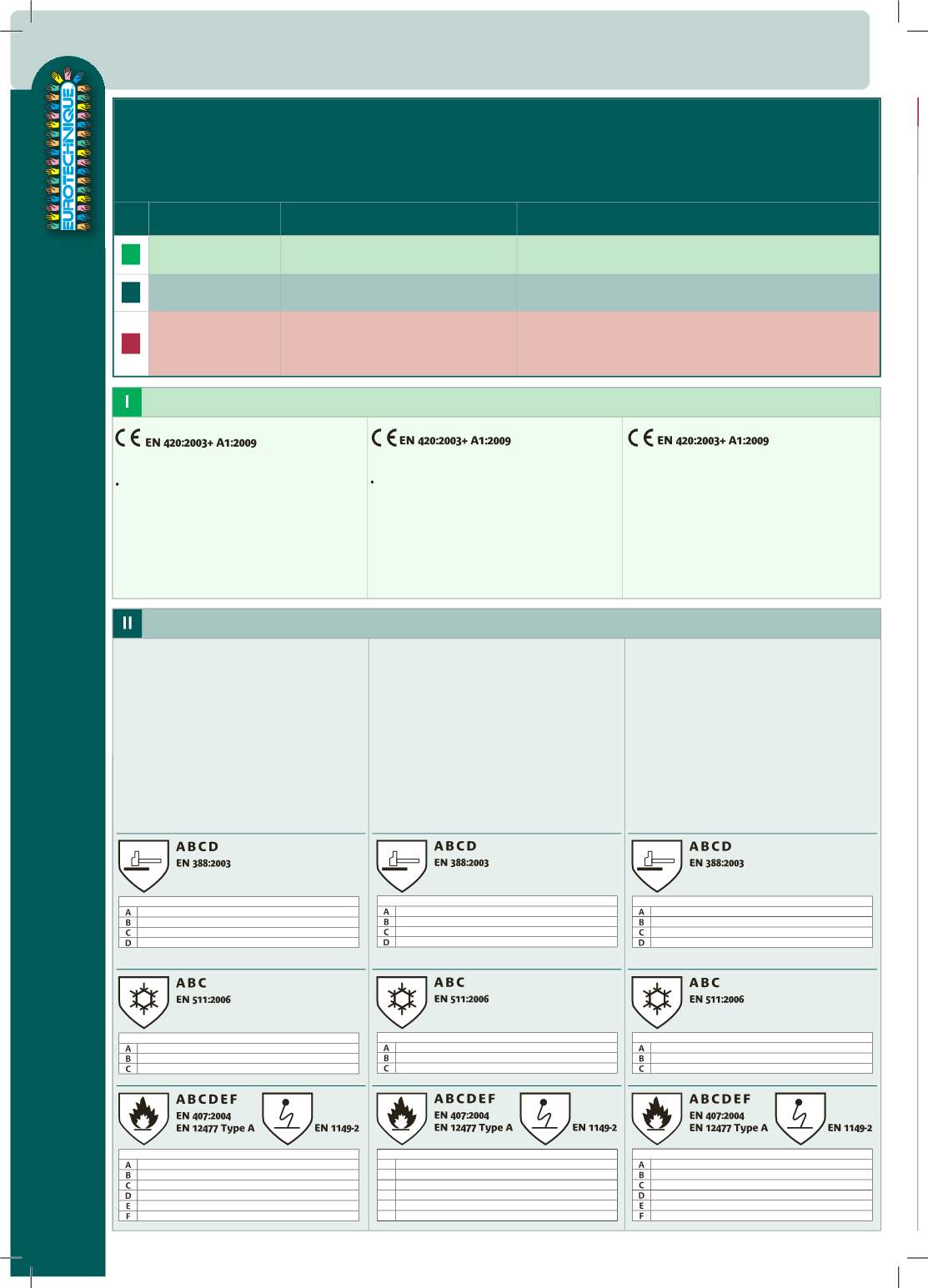
Normes, contrôles et essais
Standards, controls and testings - Normen, prüfungen und proben
Tous les Equipements de Protection Individuelle sont classés EN 3 catégories selon les risques couverts.
All indivudual protection equipments are ranged in 3 categories, according to the covered risks.
Alle PSA Ausrüstungen sind entsprechend der gedeckten Risiken in 3 Kategorien klassifiziert.
Cat. Niveau de risque
Risk level / Risikostufe
Contrôle du «type» d’EPI
Control of PPE / Prüfung des Types von PSA
Contrôle des fabrications
Control of manufacturing / Herstellungsprüfung
I
Risques mineurs
Minimal risks
Geringe Risiken
Autocertification par le fabricant
Self-certification from the manufacturer
Herstellungsbescheinigung des Herstellers
Sous la responsabilité du fabricant
Under the responsability of the manufacturer
In der Verantwortung des Herstellers
II
Risques intermédiaires
Intermediate risks
Hohe Risiken
Examen CE de Type par organisme notifié
EC type examination from a notified body
Durch Zertifizierungsstelle erstellte EG Baumusterprüfung
Sous la responsabilité du fabricant
Under the responsability of the manufacturer
In der Verantwortung des Herstellers
III
Risques irréversibles
Irreversible risks
Tödliche Gefahren
Examen CE de Type par organisme notifié
EC type examination from a notified body
Durch Zertifizierungsstelle erstellte EG Baumusterprüfung
Surveillance de fabrication par organisme notifié
(essai de produits prélevés par sondage ou système de qualité selon ISO 9000).
Notified body investigation of the manufacturing
(tests on survey products or Quality system according to ISO 9000).
Herstellungsprüfung durch Zertifizierungsstelle
(Die Produkte müssen dieAnforderungen des Qualitätssicherungssystems ISO 9000 erfüllen)
CLASSE D’EPI
CLASS OF PERSONAL PROTECTION EQUIPMENT
KLASSE DER PERSÖNLICHE SCHUTZAUSRÜSTUNG
Exigences générales pour les gants de protection
General requirements for protective gloves
Allgemeine Anforderun genan Schutzhandschuhe
Gants de protection contre les risques minimes -
Protective gloves against minimal risks - Schutzhandschuhe gegen geringe Risiken
• pH neutre (compris entre 3,5 et 9)
Innocuité (ni la construction du gant, ni les matériaux
utilisés, ni aucun dégradation résultant d’une utilisation
normale du gant ne doit en aucun cas nuire à la santé
ni l’hygiène de l’utilisateur)
• Taille
• Dextérité
• Spécificités pour les gants cuir: Teneur en Chrome IV
• Spécificités pour les gants latex: Teneur en Proteines
• Neutral pH (betweEN 3.5 and 9)
Innocuousness (neither the construction of the glove, nor
the materials used, nor any degradation consequent on the
normal use of the glove should be in any way harmful to the
health or hygiene of the wearer)
• Size
• Dexterity
• Specific for leather gloves: Chrome VI content
• Specific for natural rubber gloves: Extractable
protein content
• PH-neutral (zwischen 3,5 und 9)
• Unschädlichkeit (weder die Herstellung des
Schutzhandschuhs, noch die verwendeten Materialien,
noch jeglicher Qualitätsverlust aus dem normalen
Gebrauch des Handschuhs darf in keinem Fall die
Gesundheit oder Hygiene des Tragenden schädigen)
• Größe
• Fingerfertigkeit
• Besonderheiten für Lederhandschuhe: beinhaltet
Chrom VI
• Besonderheiten für Latexhandschuhe: beinhaltet Protein
Conformes aux exigences générales de la norme
EN 420:2003
+
classement de performances pour les caractéristiques mécaniques
d’aptitude à la fonction selon la norme
EN 388:2003
. Certains gants
font l’objet d’une norme spécifique pour des applications
particulières telles le froid (
EN511:2006
), la chaleur de contact
jusqu’à 100°C (
EN 407:2004
) et l’étanchéité (
EN 374-2:2003
).
Norme EN 12477:2001 + A1 :2005 -
Exigences minimales de
certification dans le cadre d’une protection suffisante (mains et
poignets) pour le soudage et le découpage. Exposition de courte
durée à une flamme limitée, chaleur convective, de contact,
rayonnement UV (arc, projection de métal fondu). Protection
contre les agressions mécaniques. la norme facultative
EN 1149-2
précise si le gant offre résistance minimale de 100V. Classement en
deux grands types -
Type A
: gants de moins grande dextérité mais
aux autres performances plus élevées -
Type B
: gant de plus
grande dextérité mais aux autres performances plus faibles.
Les niveaux de perf. sont classés dans un ordre croissant, niveau 0
étant le niveau le moins performant. Ces niveaux sont indiqués à
côté du pictogramme représentant la norme dans le même ordre.
Conform to the European standard
EN 420:2003
+ performance
level which shows how a glove has performed in a specific test for
the mechanical risks accordingly to the
EN 388:2003
, and by which
the results of that testing may be graded. Some gloves can also
comply with specific applications like cold (
EN511:2006
), contact
heat under 100°C (
407:2004
) and water tightness (
EN 374-2:2003
).
Standard EN 12477 :2001 + A1 :2005 -
Minimum certification
requirements for an adequate protection (hands and wrists) for
welding and cutting; Exposure of short duration to a limited flame,
convective and/ or contact heat, UV radiation (curve, melted metal
projection); Protection against mechanical attacks; The optional
EN 1149-2
standard precise whether the glove provides the
minimal resistance of 100V. Two main types -
Type A
: glove with
a lower dexterity level but with other higher performances -
Type B
: glove with higher dexterity level but with other lower
performances.
The performance levels are classed in a increasing order, level 0
being the less performing one. These levels are always indicated in
the same order next to the pictogram representing the standard.
Handschuhe gemäß der europäischen Norm
EN420:2003
haben eine
Leis-tungsklasse für die mechanischen Eigenschaften in Anpassung an ihre
Fun-ktion entsprechend der Norm
EN 388:2003
, die diese nach Testergebnis-
sen einstuft. Einige Handschuhe können zudem für spezifische
Anwendungen wiez. B. Kälte (
EN 511:2006
), Hitzekontakt bis zu 100 °C
(
407:2004
) und Wasserundurchlässigkeit (
EN374-2:2003
) genutzt werden.
Norm EN 12477: 2001 + A1: 2005
- Mindestanforderungen für die
Zertifi-zierungübereinenausreichendenSchutz (HändeundHandgelen-
ke) bei Sch-weiß- und Schneidearbeiten. Schutz vor kurzem Kontakt mit
beschränkter Flammeneinwirkung, vor konvektiver Wärme,
Kontaktwärme, UV-Strahlung (Lichtbogenschweißen), vor Spritzern
geschmolzenen Metalls. Schutz vor mechanischen Belastungen. Die
optionale Norm EN
1149-2
legt fest, ob der Handschuh einen
elektrischen Mindestwiderstand bis 100 V bietet. Klassifi-zierung in zwei
Haupttypen -
Typ A
: Handschuhe mit geringerer Beweglich-keit, dafür
aber anderweitig mit höherer Leistung -
Typ B
: Handschuhe mit höherer
Beweglichkeit, dafür aber anderweitig mit schwächerer Leistung.
Die Leistungsniveaus sind in aufsteigender Reihenfolge sortiert, Stufe 0
ist die mit der geringsten Schutzwirkung. Diese Stufen werden neben
dem Symbol für die Norm in der gleichen Reihenfolge angezeigt.
Gants de protection contre les risques intermédiaires -
Protective gloves against intermediate risks - Schutzhandschuhe gegen mittlere Risiken
Gants de protection contre les risques mécaniques
Résistance à l’abrasion (0 à 4)
Résistance à la coupure par tranchage (0 à 5)
Résistance à la déchirure (0 à 4)
Résistance à la perforation (0 à 4)
Ces niveaux sont garantis sur la paume du gant.
Protective gloves against mechanical risks
Resistance to abrasion (0 to 4)
Resistance to blade cut (0 to 5)
Resistance to tear (0 to 4)
Resistance to puncture (0 to 4)
These levels are guaranteed on the palm of the glove.
Schutzhandschuhe gegen mechanische Risiken
Abriebfestigkeit (0 bis 4)
Schnittfestigkeit (0 bis 5)
Zerreißfestigkeit (0 bis 4)
Lochwiderstand (0 bis 4)
Diese Niveaus sind auf der Handfläche des Schutzhandschuhs garantiert.
Gants de protection contre les risques de froid
Résistance au froid convectif (0 à 4)
Résistance au froid de contact (0 à 4)
Perméabilité à l’eau (0 ou 1)
Protective gloves against cold
Resistance to convective cold (0 to 4)
Resistance to contact cold (0 to 4)
Resistance to water (0 or 1)
Schutzhandschuhe vor Kälte
Widerstand gegen konvektive Kälte (0 bis 4)
Widerstand gegen Kontaktkälte (0 bis 4)
Wasserdurchlässigkeit (0 oder 1)
Gants de protection contre les risques thermiques (chaleur)
Résistance à l’inflammabilité/comportement au feu (0 à 4)
Résistance à la chaleur de contact (0 à 4)
Résistance à la chaleur convective (0 à 4)
Résistance à la chaleur radiante (0 à 4)
Résistance à de petites projections de métal en fusion (0 à 4)
Résistance à d’importantes project. de métal en fusion (0 à 4)
Protective gloves against thermal risks (heat)
A
Resistance to flammability (0 to 4)
B
Resistance to contact heat (0 to 4)
C
Resistance to convective heat (0 to 4)
D
Resistance to radiant heat (0 to 4)
E
Resistance to small splashes of molten metal (0 to 4)
F
Resistance to large splashes of molten metal (0 to 4)
Schutzhandschuhe gegen thermische Risiken
Brennverhalten (0 bis 4)
Kontaktwärme (0 bis 4)
Konvektive Hitze (0 bis 4)
Strahlungswärme (0 bis 4)
Beständigkeit gegen kleine flüssige Metallteile (0 bis 4)
Beständigkeit gegen grosse Mengen flüssiges Metall (0 bis 4)
2


